On July 12, 2018, Lan Yin research group of the school of materials, Tsinghua University published a research paper titled "A biodegradable battery for implantable transient electronic devices" in the journal SMALL. The fully biodegradable battery for self-powered transient implant is used for embedded transient electronic devices. This work not only puts forward new materials selection and preparation method in the field of degradable cell to achieve the high-performance, but the comprehensive studies about the electrical and biomedical properties even potential applications are also studied through the battery test, electrochemical analysis and degradation in vivo and in vitro experiments, functional circuit simulation, etc.
Biodegradable devices mainly refer to a kind of electronic devices with controllable degradability in physiological or environmental aqueous solutions. It is a new technical product that has attracted much attention in recent years. It can also be regarded as a branch of "transient electronics" in the biological field. The application of the device includes the execution of sensing and stimulation functions as temporary implants, as well as the important biological processes such as wound healing, tissue regeneration, etc. It can also be used as a biodegradable electronic system, which can reduce the potential risk of conventional implantable devices, chronic inflammation and reduce related medical costs. Other potential applications include environmental protection and information security.
Compared with wireless transmission and external power supply, biodegradable batteries with independent power supply capacity and high energy density are more suitable for the energy supply required for embedded devices. With a stable electrical supply, the device can achieve self-powered diagnosis and treatment in the organism, allowing induction and stimulation in the body to meet clinical standards, and can then be fully absorbed or biodegraded. In conclusion, the application of biodegradable batteries in vivo is of special significance, while the progress so far has been very limited.

FIG. 1 inside cover diagram
Yin's team has come up with a fully biodegradable cell design which can provide a high stable output voltage and an ideal capacity. The battery can drive a typical ultra-low power electronic device. It has good biocompatibility and can be completely degraded in vivo and in vitro. The battery can be used as an implantable power source, with other equipment to achieve tissue regeneration, or long time monitoring before or after surgery. The selection of electrode materials and the preparation of battery provide a suitable choice for the energy supply of implantable equipment and an important scheme for the design of complete transient electronic system.
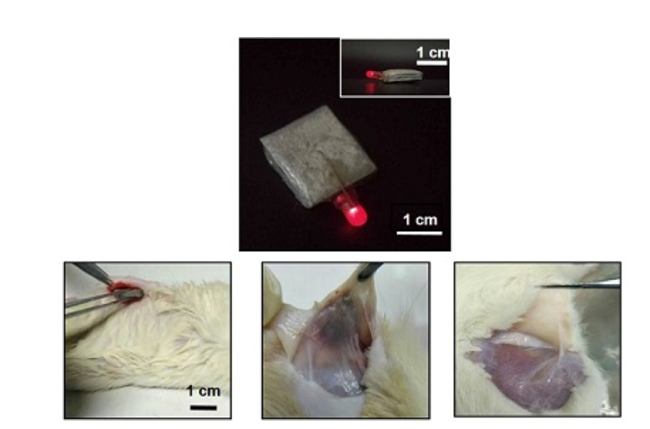
FIG. 2 Energy supply and in vivo degradation testing of high-performance degradable batteries
Prof. Yin has long been engaged in research on biodegradable materials and electronics. In addition, she also recently reported on the use of waterproof single crystal silicon film materials waterproof as biodegradable electronic encapsulation materials. With the extension of the working life of the devices, the problem regarding the encapsulation of biodegradable cortical electroencephalogram (EEG) sensors can be solved. (ACS Nano, 2017, 11, 12562-12572, DOI: 10.1021 / acsnano. 7 b06697).
The corresponding author of this article is Prof. Lan Yin, the Assistant Professor of School of Material Science and Engineering (SMSE) in Tsinghua University. And the first author is Xueying Huang, a PhD candidate SMSE, THU. Other important partners from THU include Associate Professors from SMSE, Prof. Ling-yun Zhao, and Prof. Hui Wu and Associate Professors from the Department of Electronic, Prof. Xing Sheng and Prof. Minlin Zhang. Prof. Hangxun Xu from Department of Polymer, University of Science and Technology of China also devoted to this work. SMALL, a journal published by Wiley press in Germany, currently has an impact factor of 9.598. This paper was selected as the magazine Inside Front Cover of the current month.
The paper link:https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1002/smll.201800994